Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
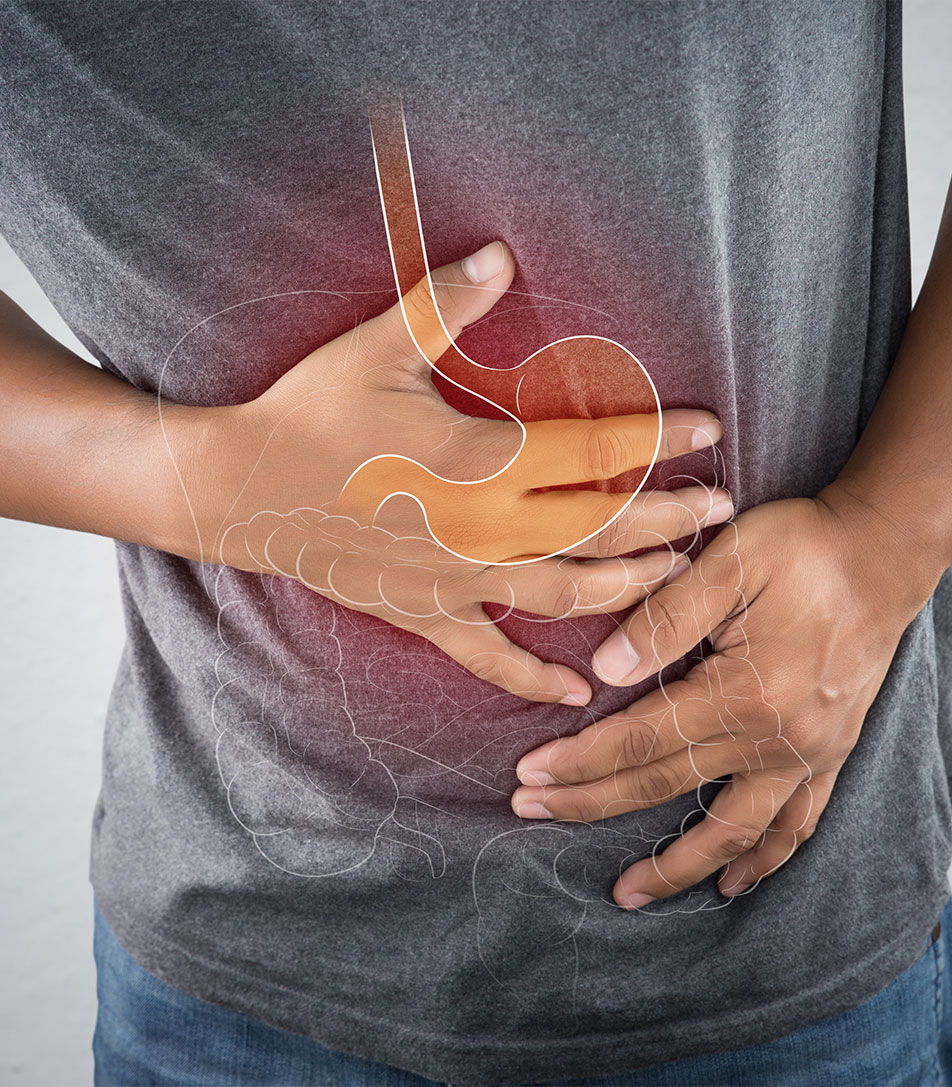
Inflammatory bowel disease, a condition that can lead to inflammation of gastrointestinal tract impacting various parts of GIT
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is comprised of two major disorders:
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease have distinct pathologic and clinical characteristics. There are theories about their pathogenesis but it still remains poorly understood.
All of the following things have been associated with inflammatory bowel disease:
- Alterations in intestinal mucus
- A high number of bacteria within the mucus
- Increased intestinal permeability
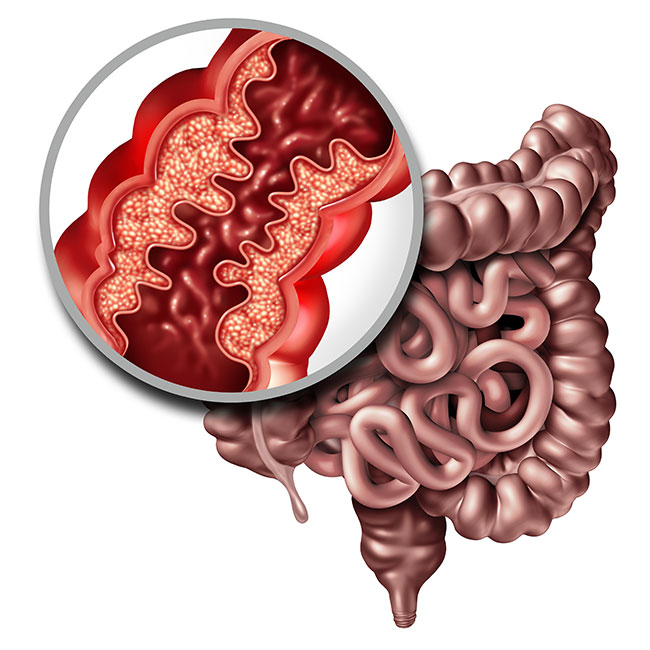
What can contribute to ibd
Dysbiosis most likely contributes to IBD
- There have been multiple large studies that link an acute gastroenteritis event to getting diagnosed with IBD within 6 months of that event
- There is a five fold increase of developing IBD after an IBS diagnosis
- There is also a noted increased risk of developing IBD within a 12 month period following a Salmonella or Campylobacter gastroenteritis
- 25 to 30 % cases of Genetic predisposity

Antibiotics and IBD

NSAIDS, Aspirin and IBD
Diet and Disease Development
Food antigens are thought to trigger an immunologic response resulting in the development of IBD. Specific pathogenic antigens have not been identified however Data is inconsistent about the exact diet that triggers IBD but a
a standard diet high in processed, fried, and sugary foods are associated with an increased risk of developing Crohn's disease, and likely also ulcerative colitis
IBD imparis Nutrient absorption
Many nutrients are absorbed by the terminal ileum
- Bile acids
- B12
- Folate
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin K
- Magnesium
Hallmark Symptoms of IBD Disease
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Prolonged diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Recatl bleeding-Specifical with Ulcerative colitis
- Urgency to defecate
How do we help ?
- Right diagnosis test (in undiagnosed cases or new cases)
- Nutrition assessment
- Right supplementation
- Anti-inflammatory protocols
- Holistic approach
- Decrease medication usage
- increase the quality of life
IBD is a chronic & replacing condition. Our program works by helping you to Understand the etiology, and pathophysiology of the disease and holistic management of ibd to improve nutrient absorption, decrease inflammation, support gut health, and help you to keep the condition in remission.
- Wellness
- Nutrition
- Home
- Functional Nutrition
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory bowel disease, a condition that can lead to inflammation of gastrointestinal tract impacting various parts of GIT
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Alterations in intestinal mucus
- A high number of bacteria within the mucus
- Increased intestinal permeability

What can contribute to ibd
- There have been multiple large studies that link an acute gastroenteritis event to getting diagnosed with IBD within 6 months of that event
- There is a five fold increase of developing IBD after an IBS diagnosis
- There is also a noted increased risk of developing IBD within a 12 month period following a Salmonella or Campylobacter gastroenteritis
- 25 to 30 % cases of Genetic predisposity

Antibiotics and IBD

NSAIDS, Aspirin and IBD
Diet and Disease Development
IBD imparis Nutrient absorption
Many nutrients are absorbed by the terminal ileum
- Bile acids
- B12
- Folate
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin K
- Magnesium
Hallmark Symptoms of IBD Disease
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Prolonged diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Recatl bleeding-Specifical with Ulcerative colitis
- Urgency to defecate
How do we help ?
- Right diagnosis test (in undiagnosed cases or new cases)
- Nutrition assessment
- Right supplementation
- Anti-inflammatory protocols
- Holistic approach
- Decrease medication usage
- increase the quality of life
